class g airspace australia
Airspace is assigned into categories which determine the level of service provided. Above the Class G ground is Class E everywhere else and is controlled airspace.

Ads B Update 2022 Where Are We Now
Sky Harbor about 15 miles outside our campus is the main commercial airport in Phoenix providing Class B airspace plus with 18 of the 92 local airports being tower controlled this allows.

. Airspace which is not Class AE. CTAF North Arrows Class F. Both IFR and VFR aircraft are permitted and neither require ATC clearance.
14 rows Class G airspace will always start at the ground and go up to 14500 msl as a. If you have been directed to contact Centre Approach or Departures after becoming. At any time this mix might include larger passenger aircraft general aviation aircraft and light sport aircraft.
A copy of the fact sheet Standardisation of Class E Airspace developed by Airservices is provided below See Related. Here VFR aircraft must maintain higher visibility and cloud. It isnt charted and it exists wherever Class A B C.
S apron twy designated for aircraft. Within Class G uncontrolled airspace some aerodromes operate a Common Traffic Advisory Frequency CTAF which imposes a requirement for radio to be carried and used but does not affect the operational services or requirements provided by air traffic services. Transition from GAAP to Class D edit Australia used to have a non-standard class of airspace for use at the capital city general aviation airports called a General Aviation Airport Procedures Zone GAAP Zone.
Generally base 8500 ft AMS Surrounding or overlying some CTR Some low-level terminal airspace when the associated TWR is closed. Up to 24 cash back What is class g airspace australia Airspace is assigned into categories which determine the level of service provided. 14 rows Class G airspace will always start at the ground and go up to 14500 msl as a maximum.
All Classes of Airspace XCSoar. In all reality Class G airspace always ends well before 14500 msl due to another layer of airspace being on top of it. Class G airspace includes all airspace below 14500 feet MSL not otherwise classified as controlled.
Class G airspace uncontrolled is that portion of airspace that has not been designated as Class A Class B Class C Class D or Class E airspace. The service provides pilots with operational information for Ballina on the aerodromes CTAF of 1242 MHz. In the airspace highlighted below Class E starts at 1200 AGL so Class G automatically starts at the surface and extends to - but doesnt include - 1200 AGL.
In most cases the airspace overlying Class G is Class E airspace. Airservices Australia is also seeking feedback on similar initiatives under Tranche 3 of the airspace modernisation project. It is proposed to lower the base of Class E airspace to 1500ft AGL in medium and high density enroute airspace between Cairns and Melbourne in 2021.
14 rows Class G airspace will always start at the ground and go up to 14500 msl as a maximum. Weather Requirements Class G minimum weather requirements exist so that you can see and avoid other aircraft and stay out of the clouds. Within continental Australia outside radar coverage above FL180 where Class A base is FL245 Within radar coverage in specifc locations or corridors under Class C or Class A airspace.
More information on classes of airspace is available. Class G airspace is uncontrolled airspace that has not been designated as Class A B C D or E. Join Online Ground School.
Daytime requirements for Class G are 1 statute mile visibility and clear of clouds to 1200ft. This airspace is uncontrolled. The only exceptions for the requirement to provide a Departure Report are.
Optional not real airspace. In Australia these range from Class A typically en route high level airspace to Class G uncontrolled airspace predominantly used by light aircraft. Primarily this is because non- controlled aerodromes in Australia can experience a high volume of traffic and host a huge diversity of aircraft types.
All aircraft flying between the surface and 8500 feet within 10 nautical miles of the airport are required to make radio calls. Non-Mandatory Radio CTAFs Class G. In Australia these range from Class A typically en route high level airspace to Class G uncontrolled airspace predominantly used by light aircraft.
The Phoenix location at the Deer Valley Airport KDVT one of the busiest airports in the world provides pilots with Class B E and Class G airspace. Benefiting the entire east coast and regional Australia they are leveraging Automatic Dependent Surveillance Broadcast ADS-B and radar surveillance assets to enhance their service delivery. Above 1200ft stays at 1sm visibility but then for cloud clearance you must be 1000ft above 500ft below and 2000ft horizontal.
More information on classes of airspace is available. Class G Airspace. The reason we put that in bold is because it is likely to appear on your written exam.
All Classes of Airspace LK8000. Australias non-controlled or CARRYING A RADIO Class G airspace is different to most parts of the world. Class g airspace australia Monday March 14 2022 Edit.
If you are a VFR aircraft and are departing the Class D Control Zone directly into Class G airspace. Class G airspace is typically the airspace very near the ground 1200 feet or less beneath class E airspace and between class B-D cylinders around towered airstrips. Mandatory Radio CTAFs Class RMZ.
As an airport in Class G airspace Ballina does not have a control tower but it does have a certified airground radio service CAGRS. Minimum flight visibility and distance from clouds required for VFR flight are contained in 14. Class G is uncontrolled airspace generally underneath and is exclusive of the Class E airspace above it.
Class C airspace associated with D293 278 is reclassified Class G SR-SS. Transition from GAAP to Class D edit Australia used to have a non-standard class of airspace for use at the capital city general aviation airports called a General Aviation Airport Procedures. Rules governing VFR flight have been adopted to assist the pilot in meeting the responsibility to see and avoid other aircraft.
This airspace is uncontrolled. There is no real Class F airspace in Australia so turn off display for Class F if North Arrows NOT required XCSoar. Metropolitan Class D formerly GAAP aerodromes do not require a Departure Report.
The Pelican Point Power Station R298 near the container terminal to the NW of Torrens Island emits a continuous plume of high temperature and high velocity gas discharges remain clear at all times. All Classes of Airspace LK8000. Class G is used wherever other classes are notalmost always from the surface to the base of the overlying Class A C D or E airspace.
This proposal is a separate initiative. In restricted airspace aircraft movements are reduced to those with certain specified permissions. The CTAF is the frequency on which pilots operating at a non-controlled.
At towered airports the class of airspace may change subject to the time of day.

How To Fly Your Drone In Controlled Airspace Dronegenuity

Lowering Of Class E Airspace In Low Density Continental Areas Engage Airservices

Australian Airspace Classification System
Controlled Airspace Overview Pilot Practice Exams Com
Controlled Airspace Overview Pilot Practice Exams Com

Class C Airspace All The Details You Need To Know Pilotmall Com
Which Radio Frequency Should Commercial Drone Pilots Be Using
Regulations Vfr Minimums Learn To Fly Blog Asa Aviation Supplies Academics Inc

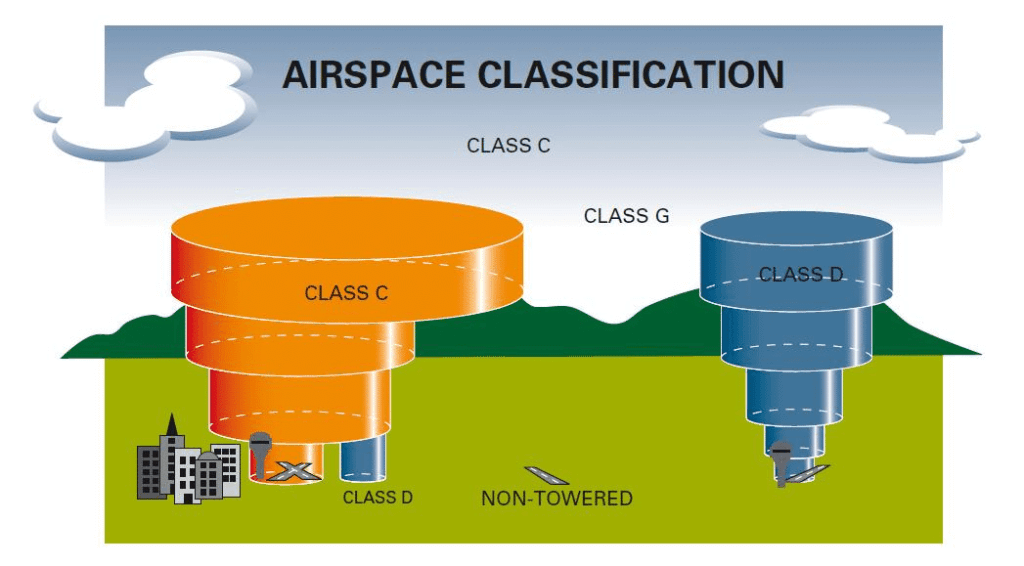
Don T Underestimate Class D Airspace Boldmethod

Airservices Proposes Lower Class E For East Coast Australian Flying

Classification Of Airspace Air Traffic Control Pilot Training Traffic

Airspace Classes Types Of Airspace Classes And How They Are Defined Atp Flight School

Understanding Class A Airspace Private Pilot Online Ground School
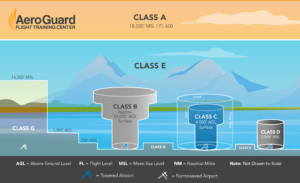
Airspace Classes How Are They Defined Aeroguard

3d Airspace Map Inside Google Earth Plus Faa Sectional Geotiffs Free Professional Land Systems Knoxville Land Surveyors

